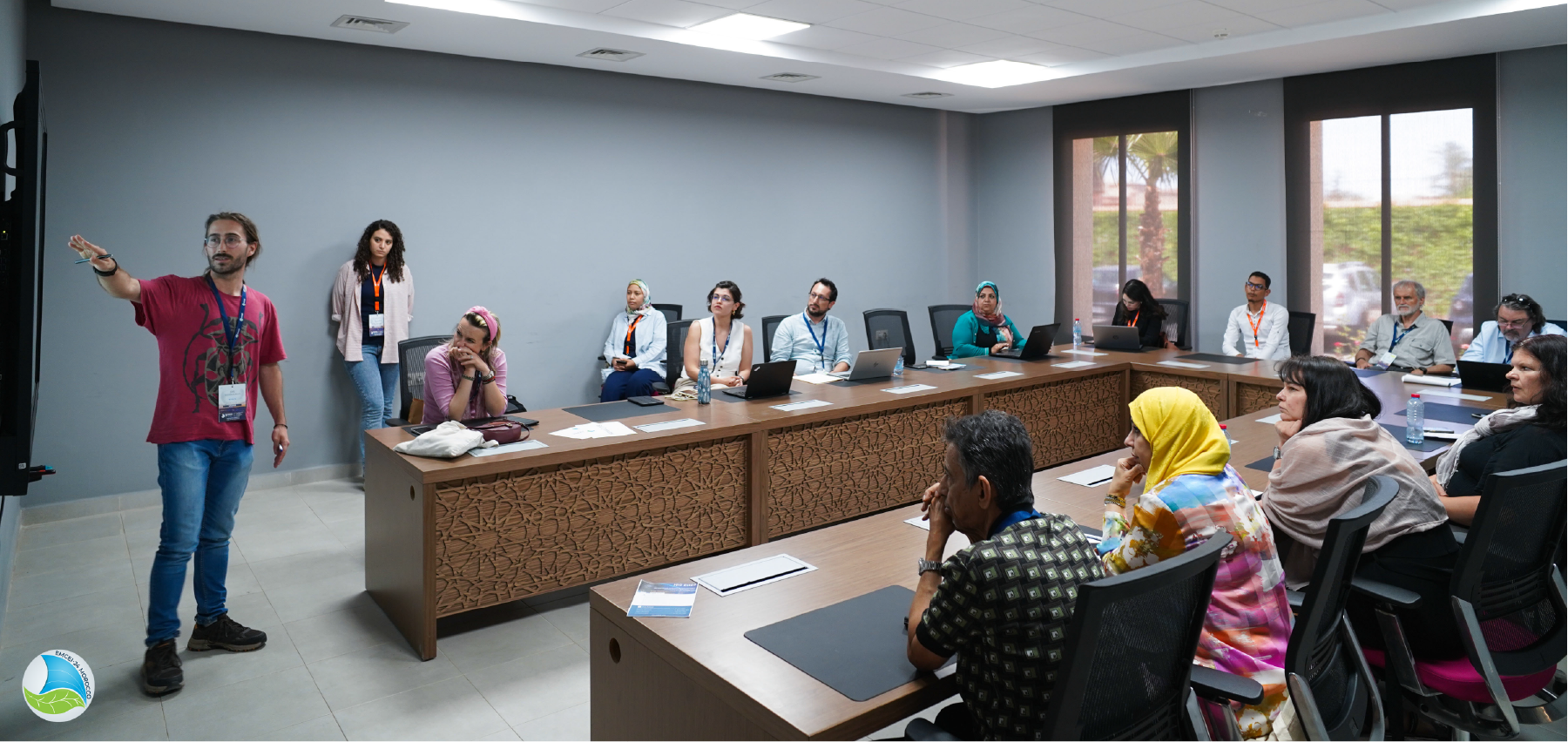
Los investigadores Sergio Martínez-Aranda y Jose Segovia-Burillo participaron en el 6th Euro-Mediterranean Conference for Environmental Integration (EMCEI 2024), celebrada el 15-18 de mayo de 2024 en Marrakesh (Marruecos). En este foro internacional centrado en la región Mediterránea, presentaron dos trabajos de alto impacto, “Assessment of post-fire soil loss due to extreme rainfall using physics-based HPC models and satellite imagery” y “Physically-based Computational Models for the Assessment of Hydraulic Soil Loss in Large-Scale Areas”, centrados en la evaluación mediante modelos numéricos de alta resolución de la erosión hidráulica y la pérdida de suelo en cuencas agro-forestales afectadas por eventos climáticos extremos, como incendios forestales. Este segundo trabajo fue reconocido con el EMCEI-24 Award a la mejor comunicación dentro del panel “Track 9 – Environmental impacts of natural hazards and environmental risk assessment”. Estos trabajos sintetizan los primeros resultados de una reciente línea de investigación desarrollada por el grupo de Tecnologías FluidoDinámicas (TFD) del I3A, en colaboración con Estación Experimental Aula Dei (EEAD) del CSIC y el Jülich Supercomputing Center (JSC) alemán.
Researchers Sergio Martínez-Aranda and Jose Segovia-Burillo participated in the 6th Euro-Mediterranean Conference for Environmental Integration (EMCEI 2024), held on May 15-18, 2024 in Marrakesh (Morocco). In this international forum focused on the Mediterranean region, they presented two high-impact papers, “Assessment of post-fire soil loss due to extreme rainfall using physics-based HPC models and satellite imagery” and “Physically-based Computational Models for the Assessment of Hydraulic Soil Loss in Large-Scale Areas”, focused on the evaluation using high-resolution numerical models of hydraulic erosion and soil loss in agroforestry catchments affected by extreme climate events, such as wildfires. This second work was recognized with the EMCEI-24 Award for the best communication within the panel “Track 9 – Environmental impacts of natural hazards and environmental risk assessment”. These works collect the first results of a recent research developed by the FluidDynamic Technologies (TFD) group of the I3A, in collaboration with the Aula Dei Experimental Station (EEAD) – CSIC and the Jülich Supercomputing Center (JSC) – Germany.